AudioSystem.java For the benefit of service providers and API implementers, a brief overview of the Java Sound source code is provided.
javax.sound.sampled.AudioSystem is the entry point to JavaSound
for obtaining resources; i.e., mixers, lines, etc. And each method of AudioSystem
involves getting the providers of some service—MixerProvider[],
FormatConversionProvider[], AudioFileReader[], or
AudioFileWriter[]. Then the method goes on to obtain some specific
information or perform some task. There is much similarity in how these methods
work. Let us take a look at how getMixerInfo() works.
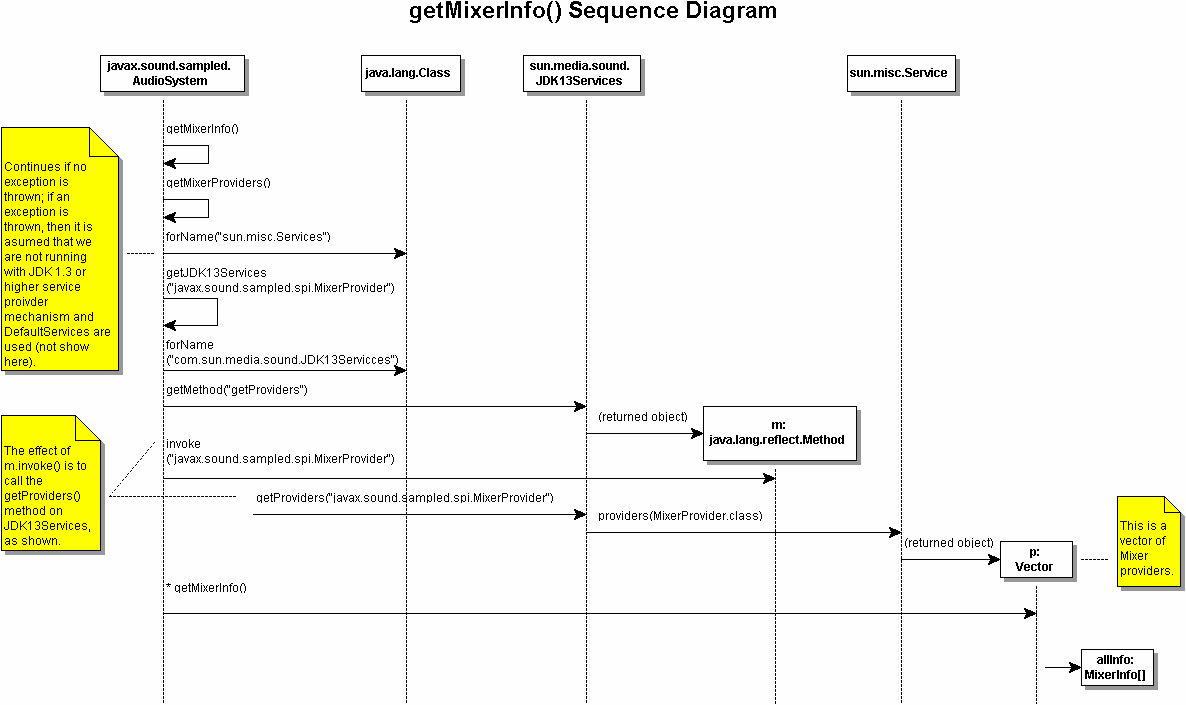
The following is a sequence diagram of getMixerInfo() in AudioSystem.java:

getMixerInfo() in AudioSystem first
calls getMixerProviders(), a private static method
of AudioSystem. The first thing that getMixerProviders()
does is attempt to load sun.misc.Service. If an exception is thrown,
it means that a pre-1.3 JRE is in use and there is no service provider lookup
mechanism present. If an exception is thrown, then sun.media.sound.DefaultServices
is used to obtain service providers (not depicted in above diagram). If the
1.3 mechanims is present, then getJDK13Serives() is called (shown
above) with "javax.sound.sampled.spi.MixerProvider" as
the argument.
getJDK13Services() is another private static
method of AudioSystem. It attempts to the load the class for "com.sun.media.sound.JDK13Services",
and if it succeeds it set Class jdk13Services equal to it. A bit
of trickery is then performed by using Class.getMethod() to get
the getProviders() method of jdk13Services, which
is returned as object Method m. The method is then invoked, which
has the effect of invoking getProviders("javax.sound.sampled.spi.MixerProvider")
on JDK13Services. This in turn uses the providers()
method of sun.misc.Service to return a vector of mixer providers,
MixerProvider[]. The getMixerInfo() method of MixerProvider
is then called on each element of the vector to return info (Mixer.info)
for all mixers of all mixer providers.
Other services are handled in a similar way. For instance, getTargetEncodings()
calls getFormatConversionProviders(), getAudioFileFormat()
calls getAudioFileReaders(), etc., which are similarly structured
to getMixerProviders().